When it comes to data analysis and statistics, it's essential to understand the difference between discrete and continuous data. Discrete data is made up of separate, distinct values that can be counted, while continuous data is a measure of quantity that is not limited to specific values. Let's take a closer look at these two types of data and their characteristics. Discrete data is usually represented by integers and whole numbers, and it can only take on specific values. For example, the number of students in a classroom or the number of goals scored in a soccer match are both examples of discrete data. This type of data is often collected through counting, and it is typically limited to a finite range of values. On the other hand, continuous data can take on any value within a range, and it is often represented by decimals or fractions. For example, the weight of a person, the height of a tree, or the temperature outside are all examples of continuous data. This type of data is often measured using instruments or equipment and can be broken down into smaller and smaller units. When analyzing data, it's important to understand the type of data you're working with so that you can use the correct statistical methods to draw conclusions. For example, if you're working with discrete data, you can use techniques like frequency distribution and probability to analyze the data. If you're working with continuous data, you'll need to use methods like probability density functions and statistical inference. At the end of the day, whether you're working with discrete or continuous data, the goal is the same: to use statistical methods to gain insight into the patterns and relationships in the data. Understanding the differences between these two types of data will help you to choose the appropriate statistical methods to use and to draw more accurate and meaningful conclusions. In conclusion, the difference between discrete and continuous data is a fundamental concept in statistics and data analysis. Discrete data is made up of separate, distinct values that can be counted, while continuous data is a measure of quantity that is not limited to specific values. Understanding these differences will help you to choose the right statistical methods to analyze your data and to draw more accurate conclusions.
If you are looking for Discrete vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples and Difference you've visit to the right place. We have 6 Pics about Discrete vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples and Difference like Numerical data are DISCRETE if the possible values are isolated points, Discrete vs Continuous Data – What’s the Difference? and also Discrete Numerical Data Definition : Discrete vs Continuous Data. Here it is:
Discrete Vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples And Difference
 intellspot.com
intellspot.com discrete continuous data vs examples definition difference comparison chart graphic
√ Discrete And Continuous Data (Definition And Examples) | Sigma Tricks
 sigmatricks.com
sigmatricks.com discrete qualitative quantitative regression
Numerical Data Are DISCRETE If The Possible Values Are Isolated Points
 www.pinterest.com
www.pinterest.com data discrete numerical values continuous possible isolated line number visit map if points range
Discrete Vs Continuous Data – What’s The Difference?
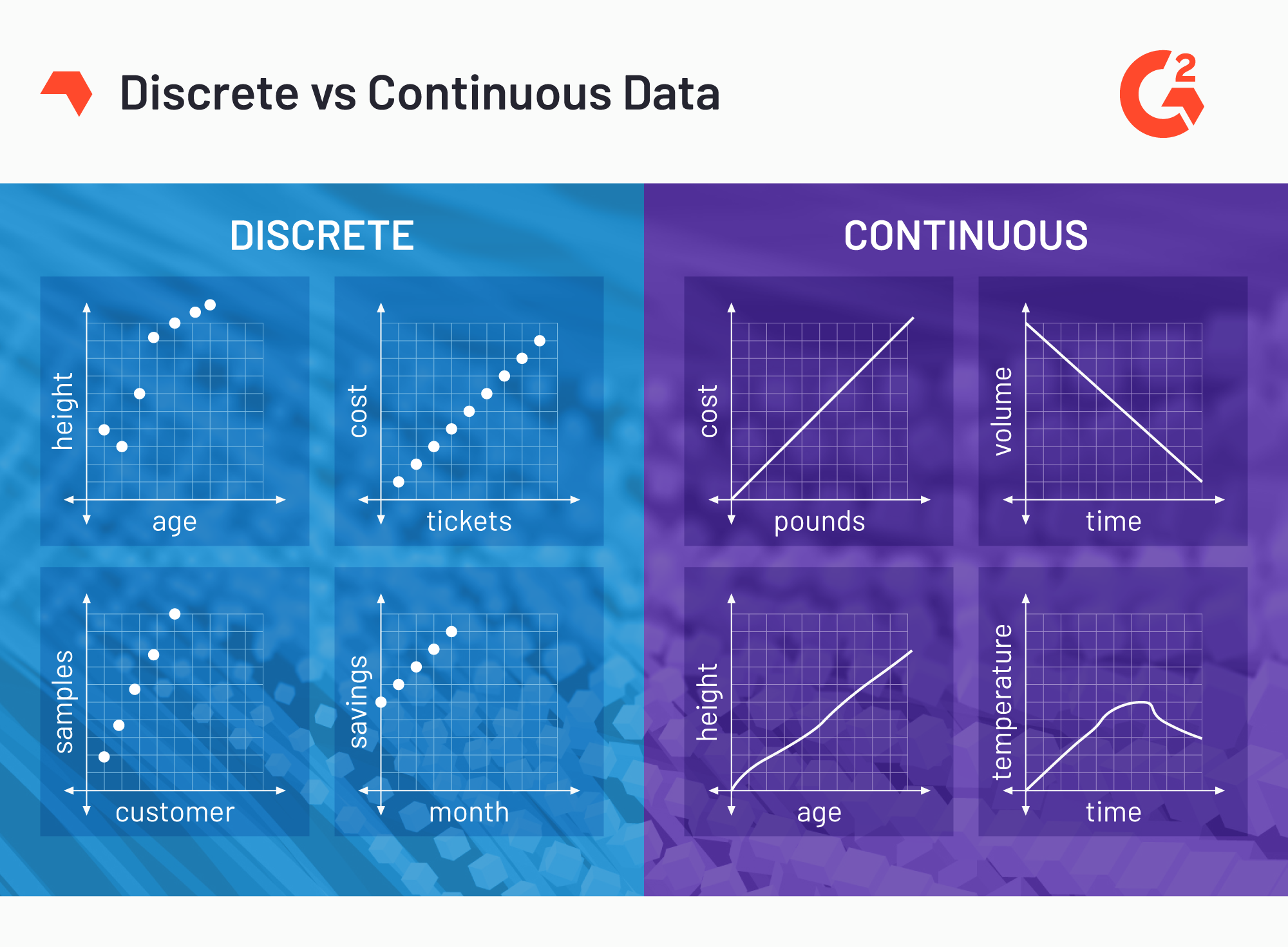 www.g2.com
www.g2.com discrete graph variables
Are Yes And No Questions Discrete Or Continuous - Hickerson Ainal1980
 hickersonainal1980.blogspot.com
hickersonainal1980.blogspot.com Discrete Numerical Data Definition : Discrete Vs Continuous Data
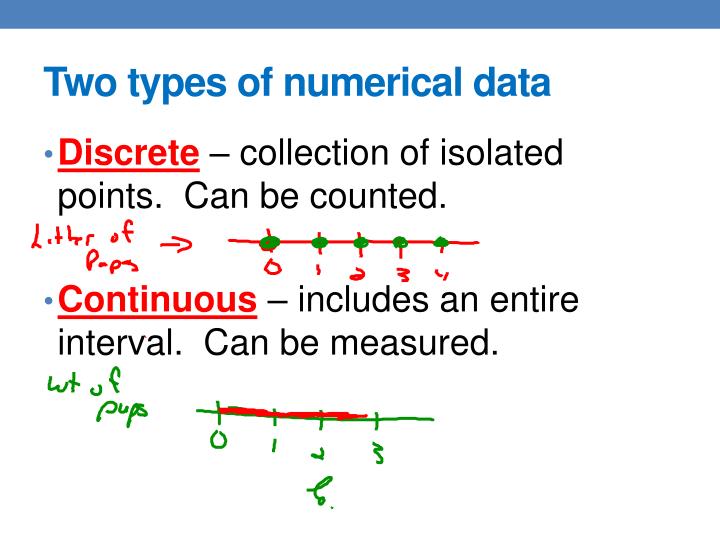 kasttank.blogspot.com
kasttank.blogspot.com numerical discrete continuous image1 slideserve
√ discrete and continuous data (definition and examples). Data discrete numerical values continuous possible isolated line number visit map if points range. Discrete graph variables
 intellspot.com
intellspot.com  sigmatricks.com
sigmatricks.com  www.pinterest.com
www.pinterest.com  www.g2.com
www.g2.com  hickersonainal1980.blogspot.com
hickersonainal1980.blogspot.com  kasttank.blogspot.com
kasttank.blogspot.com 
0 Post a Comment: