In Asian culture, mathematics has always been considered a foundational subject that is essential for success in various fields. It's no surprise then that we take a keen interest in understanding the fundamentals of mathematics and physics. In today's post, we'll be exploring two different mathematical concepts - discrete data and geometry - and how they relate to our everyday lives.
Discrete Data
Discrete data refers to numerical data that can only result in specific values. For example, the number of children in a family can only be a whole number; it cannot be 2.5 or 3.2. Discrete data can be presented visually using graphs, charts and tables. One such example is the graph below:
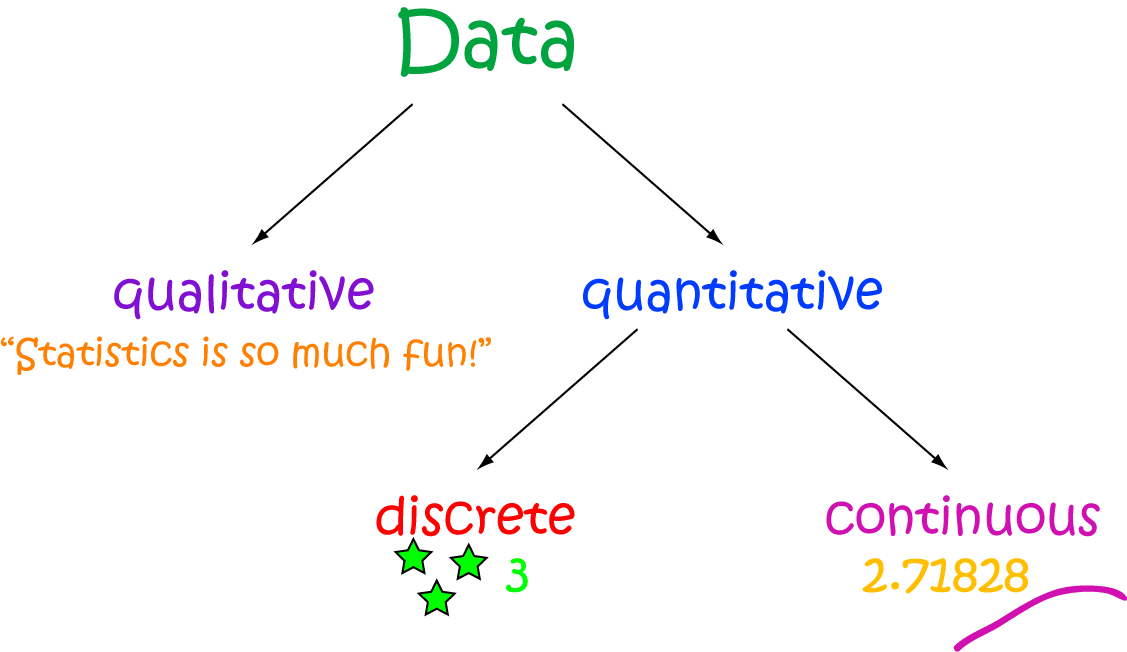
As you can see in the graph, the values on the x-axis (horizontal) are whole numbers, and the values on the y-axis (vertical) represent the frequency of occurrence for each value.
Discrete data is important in everyday life, especially in fields such as statistics, economics and healthcare. For example, the number of patients admitted to a hospital on a specific day is discrete data and can help healthcare professionals prepare for future demands.
Geometry
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, sizes, positions, and properties of objects in space. It plays a crucial role in the development of architecture, engineering and design. One area where geometry has significant importance is in the construction of buildings.
For example, the construction of a skyscraper requires not only a solid foundation but also strong load-bearing walls and beams. The designs for such structures are dependent on mathematical calculations that ensure the building can withstand environmental stresses such as wind, earthquakes, and heavy rainfall.
Another area where geometry finds utility is in computer graphics, where it is used to create 3D models of objects and environments. This technology is used in a wide range of applications, from video games to special effects in movies.
Asians have played a significant role in the development of geometry, with many famous mathematicians hailing from the continent. One notable example is Liu Hui, a mathematician from ancient China who became famous for his work on approximating π (pi), an irrational number that represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. Liu Hui's work laid the foundation for modern mathematics and helped establish the use of geometry in mathematical research.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mathematics plays an essential role in everyday life, and discrete data and geometry are two areas that have a significant impact on our world. Understanding these concepts can help us make informed decisions in our personal and professional lives and contribute to the wider fields of mathematics and physics.
If you are searching about discrete data ~ A Maths Dictionary for Kids Quick Reference by Jenny Eather you've came to the right web. We have 6 Pictures about discrete data ~ A Maths Dictionary for Kids Quick Reference by Jenny Eather like Discrete Data - Cuemath, Discrete Data - Math Definitions - Letter D and also Discrete Data - Math Definitions - Letter D. Here it is:
Discrete Data ~ A Maths Dictionary For Kids Quick Reference By Jenny Eather
discrete data example kids quantitative maths continuous days week
PPT - Section 1-3 Types Of Data PowerPoint Presentation - ID:5766273
data discrete types section continuous values numerical ppt powerpoint presentation slideserve
Discrete Data - Cuemath
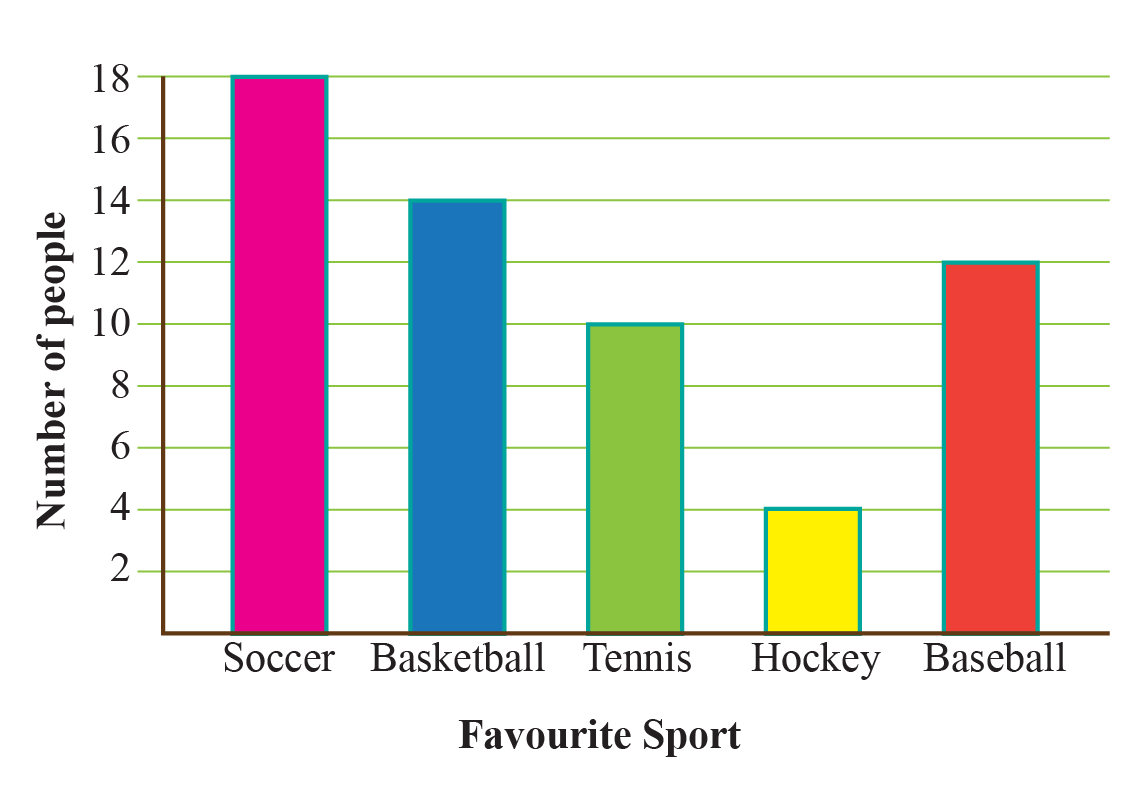 www.cuemath.com
www.cuemath.com discrete representation graphical therefore
Discrete Data - Cuemath
 www.cuemath.com
www.cuemath.com discrete observe graphical modes
Pin By Curvature Of The Mind On Physics & Math Yo | Pinterest
discrete data continuous numerical values math number lines line interval points innovativegis physics types if mathematics
Discrete Data - Math Definitions - Letter D
 www.subjectcoach.com
www.subjectcoach.com discrete data continuous definition math numbers example values number value certain only real definitions letter
Discrete data continuous numerical values math number lines line interval points innovativegis physics types if mathematics. Discrete data. Discrete data example kids quantitative maths continuous days week
0 Post a Comment: