Numerical data are important for many fields, including science, economics, and finance. Understanding the scale of measurement used to collect numerical data is key in analyzing and interpreting data. In this post, we will cover some basic concepts of scale of measurement.
Types of Scale of Measurement
There are four types of scales of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. They differ according to the nature of the values that are used to make measurements, and how these values are related to one another.
Nominal Scale
Nominal scales provide labels or names for objects, but do not provide any inherent order. For example, colors, genders, or political affiliation are nominal variables.

In the above image, we see that numerical data is discrete if the possible values are isolated points. This means that values are distinct and separated from one another. Nominal scales use discrete values, because they provide only labels and do not have a natural ordering.
Ordinal Scale
Ordinal scales provide an ordering for the values measured, but the differences between the values cannot be meaningfully determined. For example, the ranking of students in a class, or the order in which runners finish a race are ordinal variables.
Interval Scale
Interval scales provide an ordering for the values measured, and the differences between the values are meaningful, but there is no true zero point. For example, temperature measured in Celsius or Fahrenheit is an interval variable.
Ratio Scale
Ratio scales provide an ordering for the values measured, and the differences between the values are meaningful, and there is a true zero point. For example, height, weight, or income are ratio variables.
Conclusion
Understanding the different scales of measurement is important for analyzing and interpreting numerical data. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales each have unique characteristics that make them suitable for certain types of data. By understanding the nature of the data being measured, researchers can ensure that they are using the appropriate scale of measurement for their analysis.
If you are searching about Discrete vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples and Difference you've came to the right place. We have 6 Pics about Discrete vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples and Difference like Discrete vs Continuous Data – What’s the Difference?, Discrete vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples and Difference and also Basic concepts of scale of measurement. Here it is:
Discrete Vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples And Difference
 intellspot.com
intellspot.com discrete numerical intellspot quantitative
Discrete Vs Continuous Data – What’s The Difference?
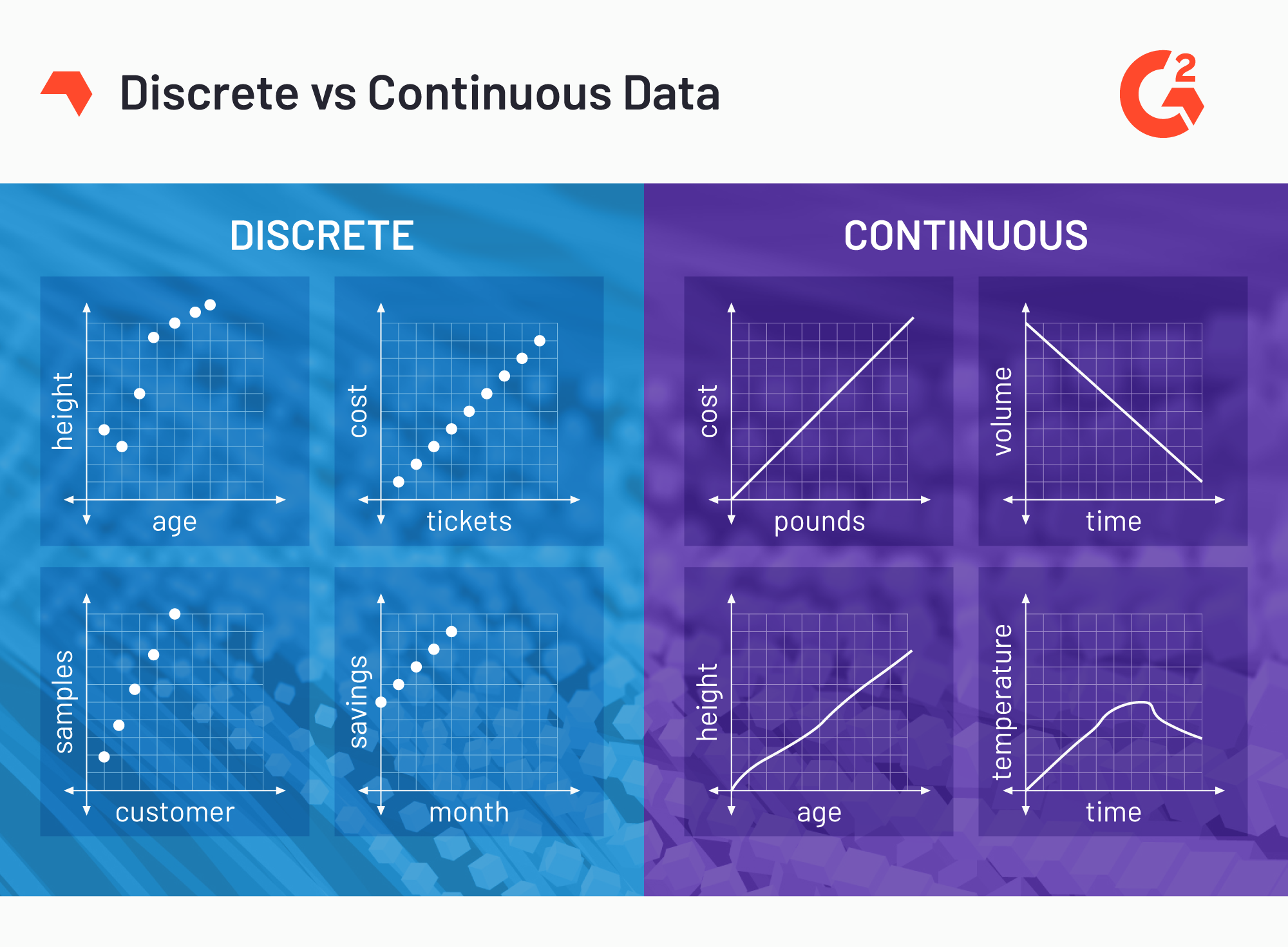 www.g2.com
www.g2.com discrete graph variables
Numerical Data Are DISCRETE If The Possible Values Are Isolated Points
 www.pinterest.com
www.pinterest.com data discrete numerical values continuous possible isolated line number visit map if points range
Discrete Vs Continuous Data: Definition, Examples And Difference
discrete continuous data vs examples definition difference chart comparison infographic diferences pdf
Basic Concepts Of Scale Of Measurement
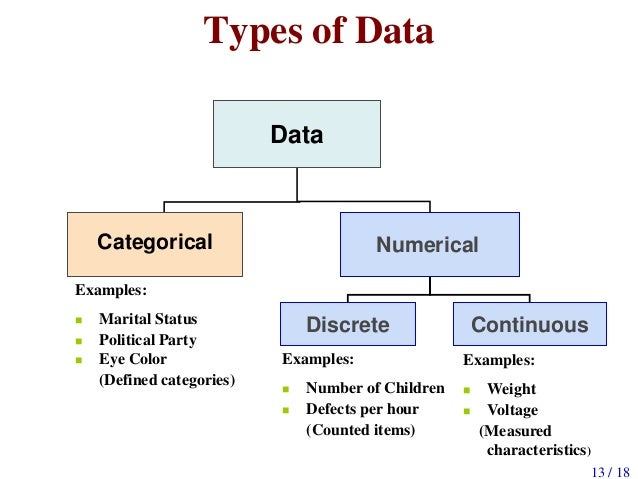 www.slideshare.net
www.slideshare.net discrete categorical numerical
Continuous Vs Discrete Data - YouTube
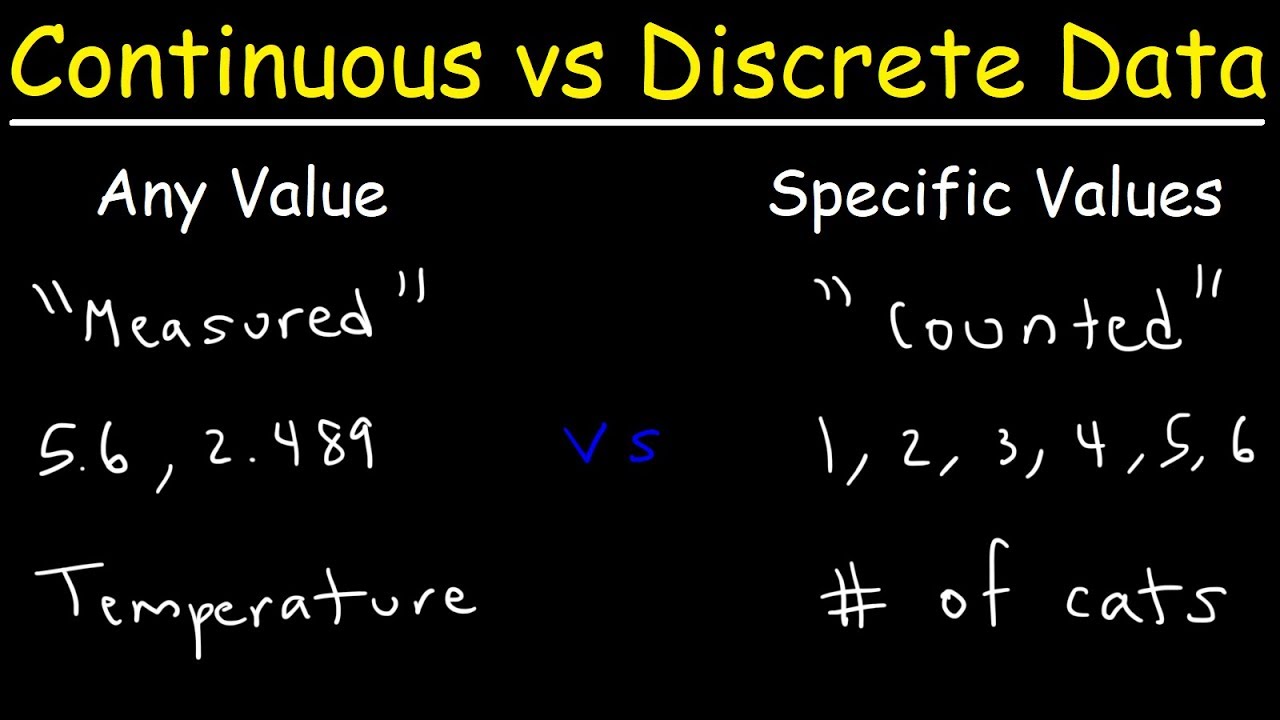 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com discrete
Discrete categorical numerical. Numerical data are discrete if the possible values are isolated points. Discrete vs continuous data: definition, examples and difference

0 Post a Comment: