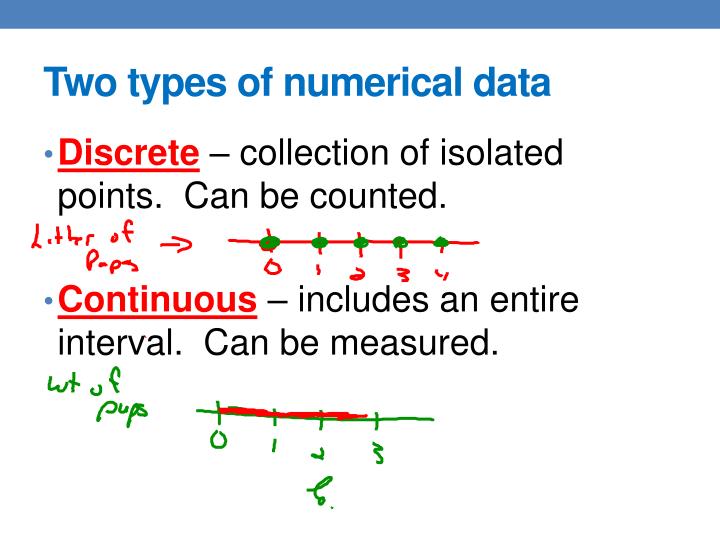
Discrete Numerical Data Definition : Discrete vs Continuous Data
Discrete numerical data refers to data that can only take on specific values, usually integers. Examples of discrete data include the number of cars in a parking lot, the number of students in a class, and the number of goals scored in a soccer game.

Introduction To Statistics
Statistics and data analysis are critical components of understanding and solving problems in various fields, including finance, social sciences, and technology. Today, we will explore two types of numerical data - discrete and continuous data.
If you are searching about Introduction To Statistics you've visit to the right page. We have 6 Pics about Introduction To Statistics like Discrete Numerical Data Definition : Discrete vs Continuous Data, Pin by curvature of the mind on Physics & Math yo | Pinterest and also Discrete Numerical Data Definition : Discrete vs Continuous Data. Here it is:
Introduction To Statistics
 www.slideshare.net
www.slideshare.net discrete continuous
Discrete Numerical Data Definition : Discrete Vs Continuous Data
 kasttank.blogspot.com
kasttank.blogspot.com numerical discrete continuous image1 slideserve
Episode 4 ~ Continuous And Discrete Graphs - YouTube
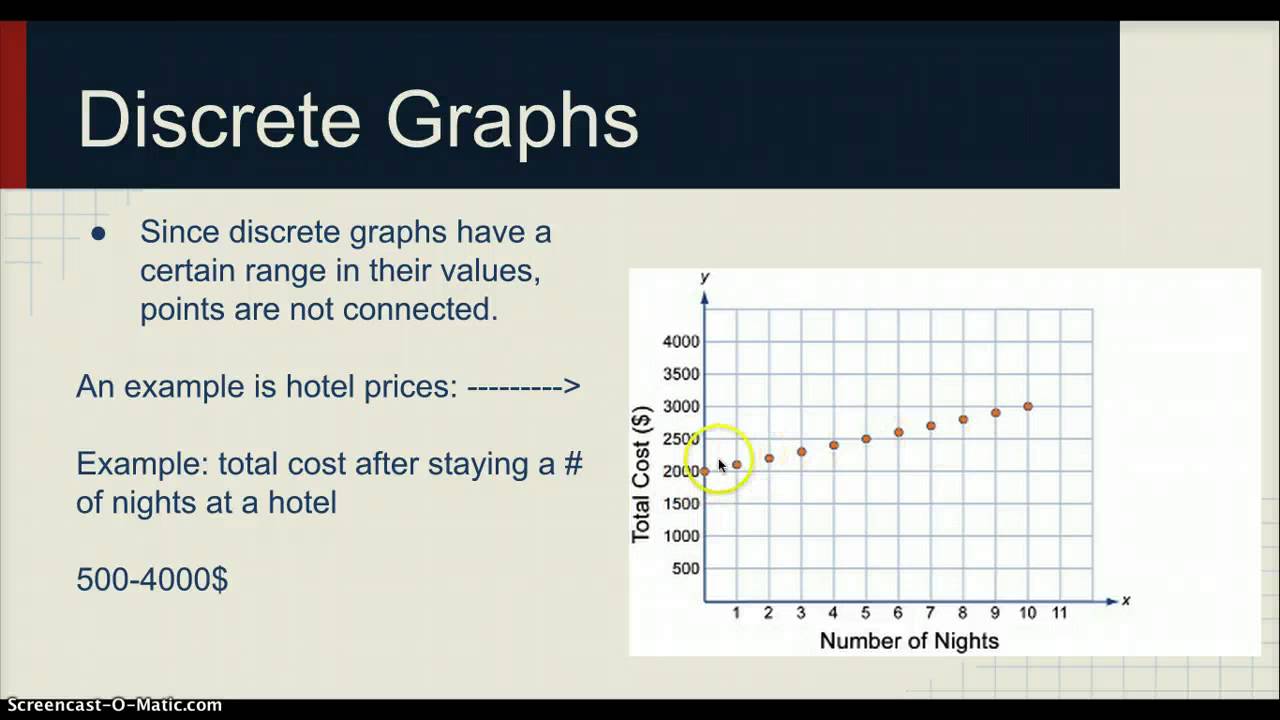 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com discrete continuous graphs
Statistics In Pharmaceutical Sciences
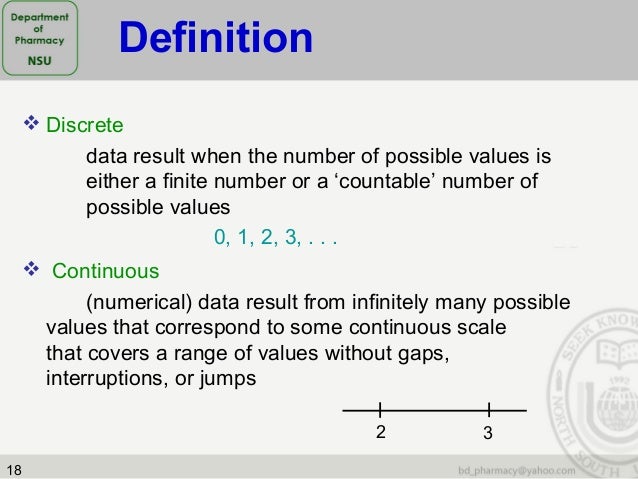 www.slideshare.net
www.slideshare.net statistics discrete values pharmaceutical
Discrete Vs Continuous Data – What’s The Difference?
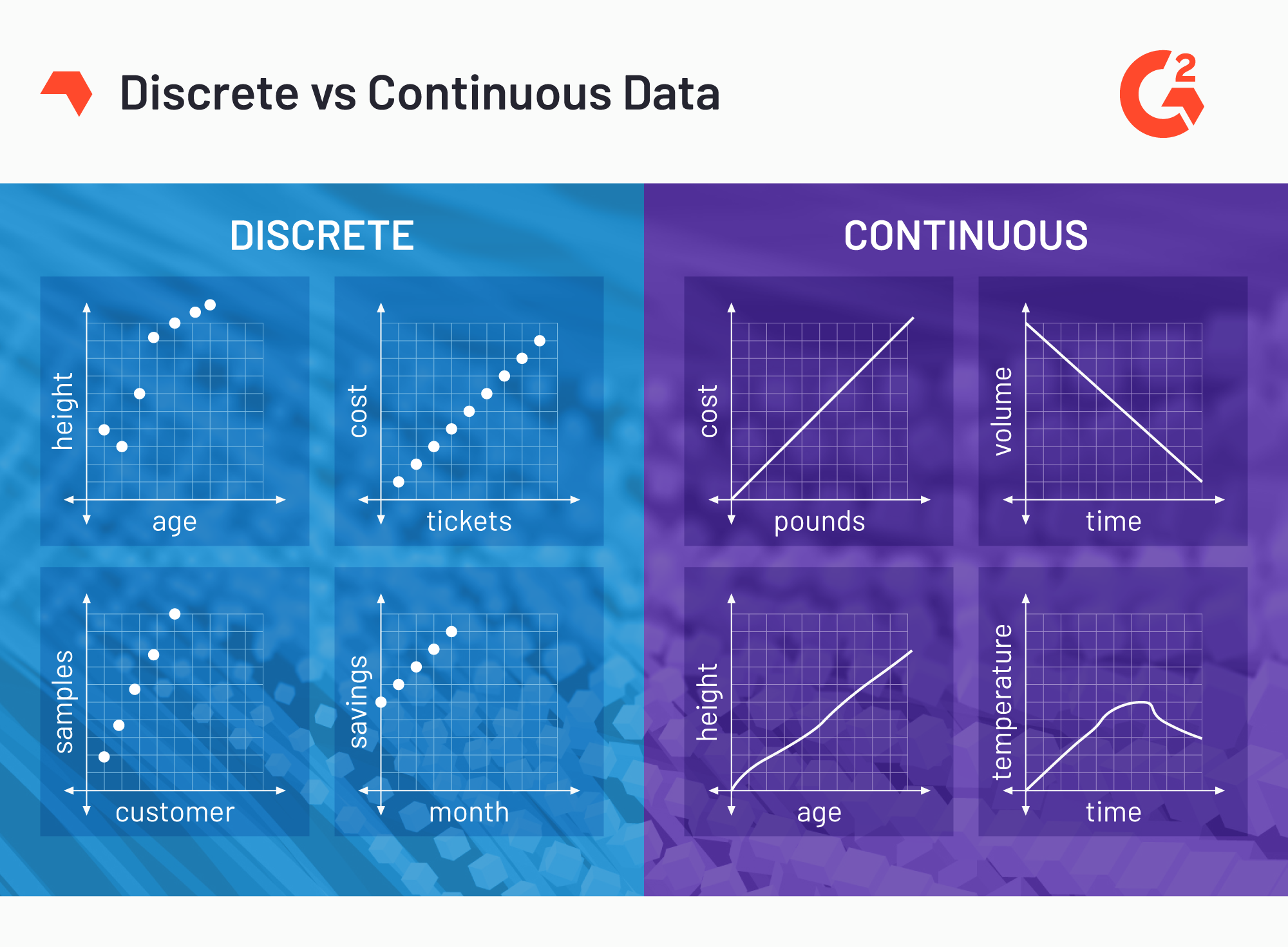 www.g2.com
www.g2.com discrete graph variables
Pin By Curvature Of The Mind On Physics & Math Yo | Pinterest
discrete data continuous numerical values math number lines line interval points innovativegis physics types if mathematics
Pin by curvature of the mind on physics & math yo. Statistics discrete values pharmaceutical. Episode 4 ~ continuous and discrete graphs
![best discrete math book reddit [book] discrete mathematics and it's
application by kenneth h. rosen](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgX8KPlQ5CEG1mZ7CZOWYU2t5aigoV-QvtwuSD64R3o6l5-Oi18JiwYrcN8eXBFuBZR0wg-f3fa2CPx1WW5LotESV4FvwN6f2VtrTtXHa4R56o-HVC8857_eTyuNaBRBMWJmhVsJsn2V0X2/s72-c/discrete-mathematics-and-its-applications-700x700-imadd3ghfzkufhz3.jpeg)

0 Post a Comment: